Trees
test
Trees are usually represented by nodes. There are different ways to represent a node in a tree:
Terminology
- root - the most parent node. The First.
- height - the longest path from the root to the most child node.
- binary tree - a tree in which has at most 2 children, at least 0 children
- general tree - a tree with 0 or more children
- binary search tree - a tree in which has a specific ordering to the nodes and at most 2 children
- leaves - a node without children
- balanced - a tree is perfectly balanced when any node's left and right children have the same height.
- branching factor - the amount of children a tree has.
- How it works
- Big(O)
It's O(N)
Traversals
There are different ways in which you can visit the nodes of a tree. And these types of traversals are known as DFS (depth first search or depth first traversal)
Breadth First Search
- How it works
Breadth First Search is kinda like the opposite of a depth frist search. Breadth first search will goind to visit first node, then it's gonna visit first node in next row, then secound node in first row, then first node in secound row and so on.
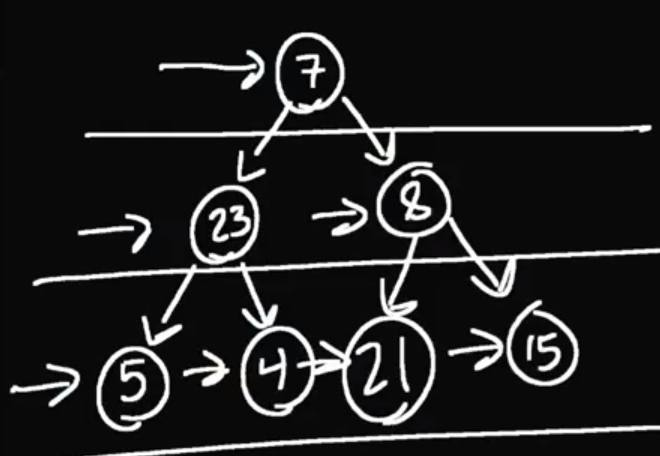
Let's draw this out again using a queue.
So we are starting with 7. First node have value 7 and children 23 and 8. So In Queue we are adding, 23 and 8. Now Queue looks like this 7 -> 23 -> 8. Because node with value 7 doesnt have any other children then we will pop off 7 and print out 7. Then we will visit node with value 23. 23 have two children 5 and 4 so we will add them to queue now our queue is 23 -> 8 -> 5 -> 4. Then we will pop up 23 and print out 23. Now it is [7,23].Next in queue is 8, then we will visit his children. We will repeat this until we dont have value in our queue. End array will be [7,23,8,5,4,21,15]
- Big(O)
Big O for Beadth First Search is O(N) but if we using javascript array then it will be O(N^2)
Diferance between depth first search vs breath first search.
Depth first search does preserve shape, wheareas breath first search does not.
- complete tree is where all left and right is completely filled and it has the same height.
- non-complete tree is oposite of complete tree.
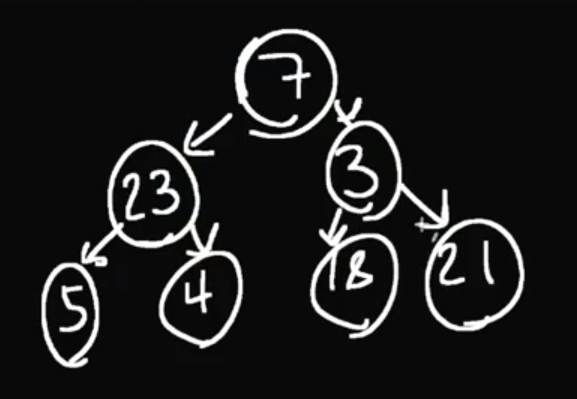
- pre order - [7,23,5,4,3,18,21]
- in order - [5,23,4,7,18,3,21]
- post order - [5,4,23,18,21,3,7]
Find value (Binary search tree)
- How it works
Because we know that left side is smaller value of parrent value and right side is bigger then value, then we know what path to choose to find our value.
Binary search tree is still binary tree, but there is a rule that has to be applied at every node. Left side has to be less then or equal to parrent value and right side has to be greater than parrent value.
- Big(O)
It's between O(logN) and O(N) . N is height of tree.
Example below is to check if two binary trees is equal in shape and in strucutre.
Insert value
- How it works
Insertion is a lot like find.
Before we want to insert some value, we need to find location where to insert it. On that way we will preserve the rule of the binary tree.
Left subtree will be less then or equal to parent value, and right subtree will be bigger then parent value.
- Big(O)
It's between O(logN) and O(N) . N is height of tree.
Delete value
- How it works
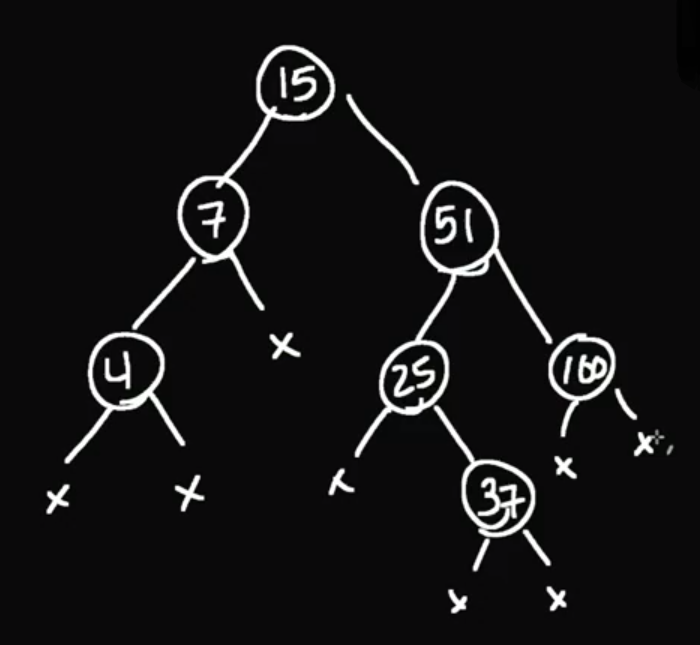
We need to preserve the rule of the binary tree and there are multiple scenario what can happend because of that:
If we want to remove number 4. Because 4 does not have any children, then tree will be still valid.
case 1: no child -> just delete
If we want to remove 7. Then we will make 15 to point to 4 to tree be valid.
case 2: one child -> set parent to child
If we want to remove 51 we first need to find largest value from left side or smallest value from the right side. Then we will put that item on position where we want to remove value. You will chose one path or another base on maximum height of that subtree. You can remove from side were is bigger height to shrink tree.
case 3 two child ->